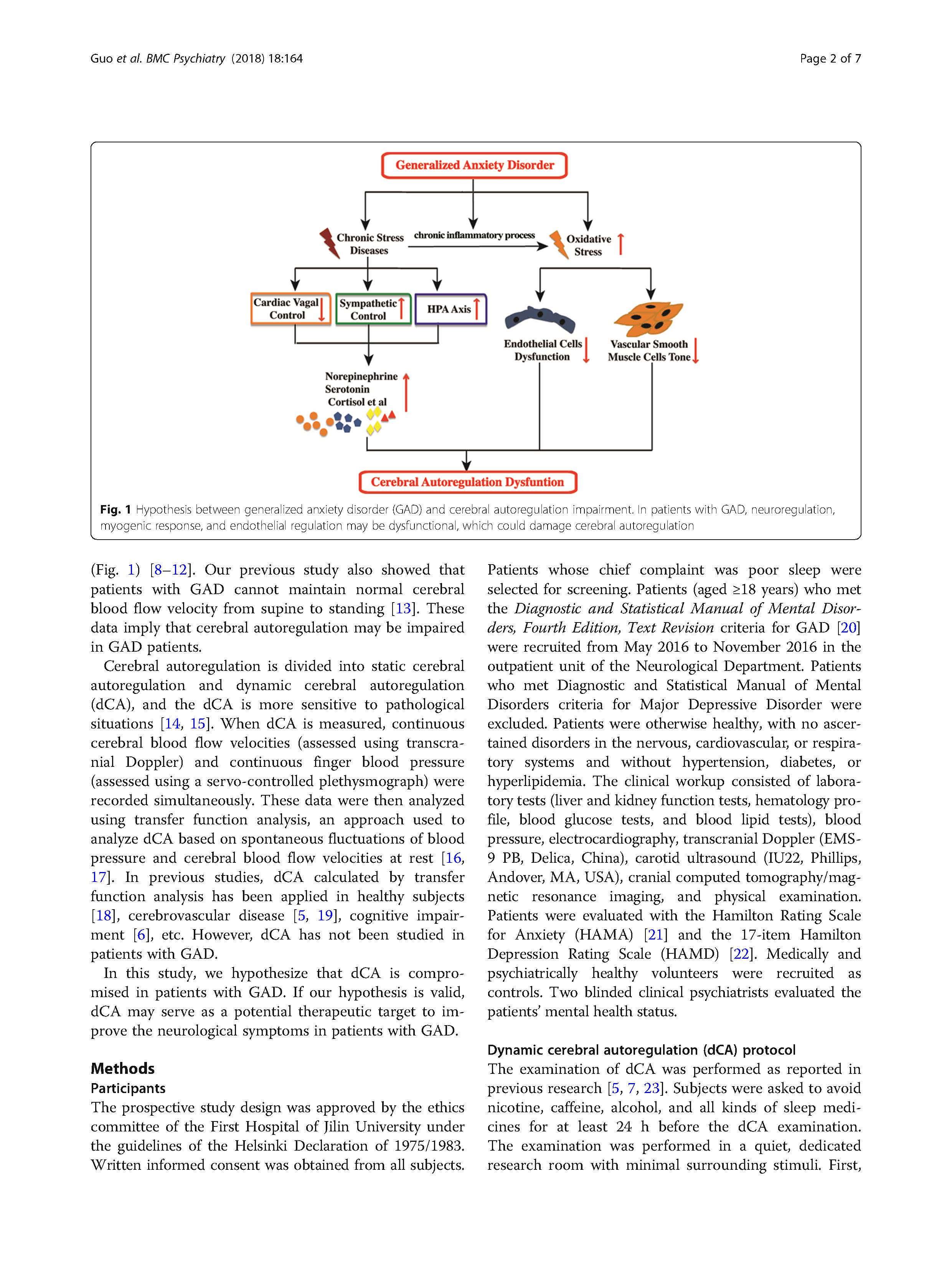
Understanding the Impact of PET Scan Radiation Dose on Patient Safety and Diagnostic Accuracy
#### PET Scan Radiation DosePositron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are vital diagnostic tools in modern medicine, particularly in oncology, cardiology, an……
#### PET Scan Radiation Dose
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are vital diagnostic tools in modern medicine, particularly in oncology, cardiology, and neurology. However, a common concern among patients and healthcare providers is the PET Scan Radiation Dose associated with these procedures. This article aims to explore the implications of radiation exposure during PET scans, focusing on safety, effectiveness, and advancements in technology that help mitigate risks.
#### What is a PET Scan?
A PET scan is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows doctors to observe metabolic processes in the body. During the procedure, a small amount of radioactive material is injected into the patient, which emits positrons. These positrons collide with electrons in the body, producing gamma rays that are detected by the PET scanner to create detailed images. The PET Scan Radiation Dose is a crucial factor, as it varies depending on several elements, including the type of scan, the patient's body weight, and the specific radioactive tracer used.

#### Understanding Radiation Dose
Radiation dose is typically measured in millisieverts (mSv). For a PET scan, the average radiation dose ranges from 5 to 25 mSv, depending on the factors mentioned earlier. To put this into context, a single chest X-ray exposes the patient to about 0.1 mSv, while a CT scan of the abdomen may expose the patient to approximately 10 mSv. While the PET Scan Radiation Dose may seem high, it is essential to weigh the benefits of accurate diagnosis against the potential risks of radiation exposure.
#### Safety Considerations

The safety of patients undergoing PET scans is a top priority for healthcare providers. The radiation dose is carefully calculated to ensure that it is as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA principle). Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of new tracers that require lower doses of radiation while still providing high-quality images. Patients are encouraged to discuss any concerns about radiation exposure with their healthcare providers, who can provide personalized information based on individual health conditions and the necessity of the scan.
#### Advancements in Technology
Recent innovations in imaging technology have contributed to reducing the PET Scan Radiation Dose without compromising diagnostic accuracy. Techniques such as time-of-flight (TOF) imaging and improved reconstruction algorithms have enhanced image quality, allowing for lower doses of radioactive tracers. Furthermore, hybrid imaging systems, such as PET/CT and PET/MRI, combine multiple imaging modalities to provide comprehensive diagnostic information while minimizing radiation exposure.
#### Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the PET Scan Radiation Dose is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. While there are inherent risks associated with radiation exposure, the benefits of accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning often outweigh these risks. Continuous advancements in technology and a commitment to patient safety ensure that PET scans remain a vital tool in modern medicine. Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and discuss any concerns regarding radiation exposure with their healthcare team, ensuring informed decisions about their health and well-being.