Heloc Tax Deductibility: Your Guide to Maximizing Loan Benefits
Guide or Summary:Understanding Heloc Loan Tax DeductibilityEligibility for Tax Deductions on Heloc LoansCalculating the Tax Deductibility of a Heloc LoanStr……
Guide or Summary:
- Understanding Heloc Loan Tax Deductibility
- Eligibility for Tax Deductions on Heloc Loans
- Calculating the Tax Deductibility of a Heloc Loan
- Strategies for Maximizing Tax Deductibility on Heloc Loans
When it comes to homeownership, a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) can be a powerful financial tool. Beyond its flexibility in accessing funds, one of the lesser-known benefits of a HELOC is its potential tax deductibility. This article delves into the intricacies of using a HELOC for tax savings, exploring how you can leverage this feature to enhance your financial situation.
Understanding Heloc Loan Tax Deductibility
A HELOC is a revolving line of credit that allows homeowners to borrow against their equity. While the primary use of a HELOC is for home improvement projects, it can also be used for any purpose, including consolidating debt, covering medical expenses, or even as a source of emergency funds.
The tax deductibility of a HELOC stems from the interest payments made on the loan. These payments can be deducted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe. This deduction is particularly beneficial in years when you've made significant improvements to your home or have incurred high levels of debt.
Eligibility for Tax Deductions on Heloc Loans
Not all HELOCs are created equal, and the tax deductibility of your loan hinges on several factors. Firstly, ensure that your HELOC is secured by your primary residence or second home. Additionally, the loan must be used for qualified expenses, such as home repairs, improvements, or refinancing to lower interest rates.
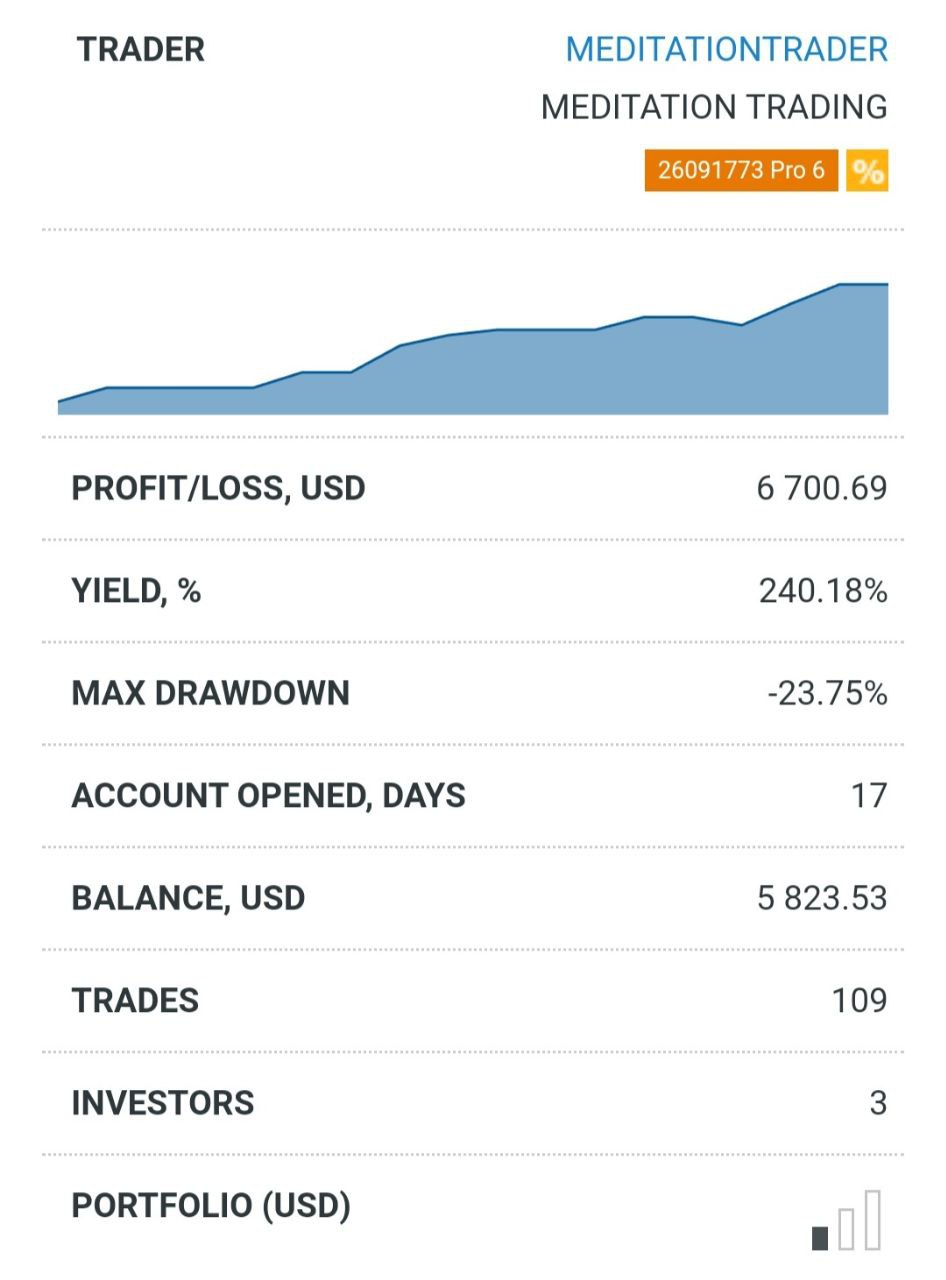
Moreover, the IRS requires that you itemize your deductions to claim the interest paid on your HELOC. This means you must decide whether the deduction from your mortgage interest is greater than the standard deduction. If it is, itemizing your deductions may yield significant tax savings.
Calculating the Tax Deductibility of a Heloc Loan
Calculating the exact tax savings of a HELOC can be complex, as it depends on a variety of factors, including your income level, mortgage interest rates, and the amount of equity in your home. However, a general approach involves adding up the interest payments made over the year and comparing this to your income tax liability.
For example, if you paid $5,000 in interest on your HELOC and your taxable income was $50,000, the interest deduction would reduce your taxable income to $45,000. Assuming a tax rate of 22%, your tax savings from the $5,000 in interest would amount to $1,100.
Strategies for Maximizing Tax Deductibility on Heloc Loans
To make the most of your HELOC's tax deductibility, consider the following strategies:

1. **Timing Your Repayments**: Paying off your HELOC before the end of the year can maximize your tax deduction. If you're expecting to be in a higher tax bracket next year, it might make sense to accelerate your payments and claim the deduction now.
2. **Utilizing the Full Credit**: Make sure to utilize the full amount of your HELOC's credit line for qualifying expenses. The more interest you pay, the greater your tax deduction.
3. **Keeping Detailed Records**: Maintain accurate records of all your HELOC transactions, including interest payments and any withdrawals. This documentation will be crucial when it comes time to claim your deductions.
4. **Consulting a Tax Professional**: Tax laws can be complex, and the rules surrounding HELOC tax deductibility can vary based on individual circumstances. Consulting with a tax professional can help ensure you're maximizing your deductions and staying compliant with IRS regulations.
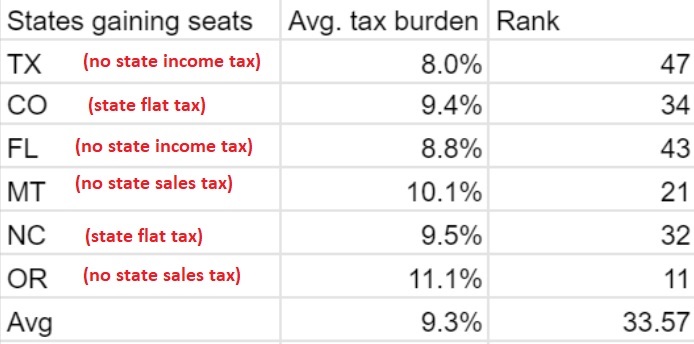
In conclusion, a Home Equity Line of Credit can be a powerful tool for homeowners, offering flexibility and access to funds when needed. By understanding how to utilize the tax deductibility of a HELOC, you can enhance your financial situation and potentially reduce your tax liability. With careful planning and record-keeping, you can make the most of this valuable financial resource.